Effectively storing JSON in relational databases using json-schema
You are building a system using some relational database and you are face to face with a problem. The problem is that the data is a bit unstructured and you are having trouble trying to figure out how to store the data in a relational database. The obvious answer coming to your mind is using a JSON to store this data. Yes, many of the relational databases are now supporting JSON and this can be a great way to solve this problem.
What can go wrong here? JSON is open, JSON is flexible. We need to have some validations before adding the JSON data to the database because we do not want irregular, inconsistent or wrong data. If we can have something where we define how we want our JSON to be, more like rules and we validate this with our incoming JSON data, that can save us from the data inconsistency problem. This is where JSON Schema comes in.
JSON Schema is a vocabulary that allows you to annotate and validate JSON documents.
Give me an example
We are building a simple survey app using Django REST Framework. Let's note down the requirements.
- One survey can have n number of questions. We will be supporting 8 types of questions.
- A survey can be in the drafted state or the published state.
- Once a survey is published, users can fill the survey.
The table design is shown below. If you are not familiar, this is how we define the database table in Django.
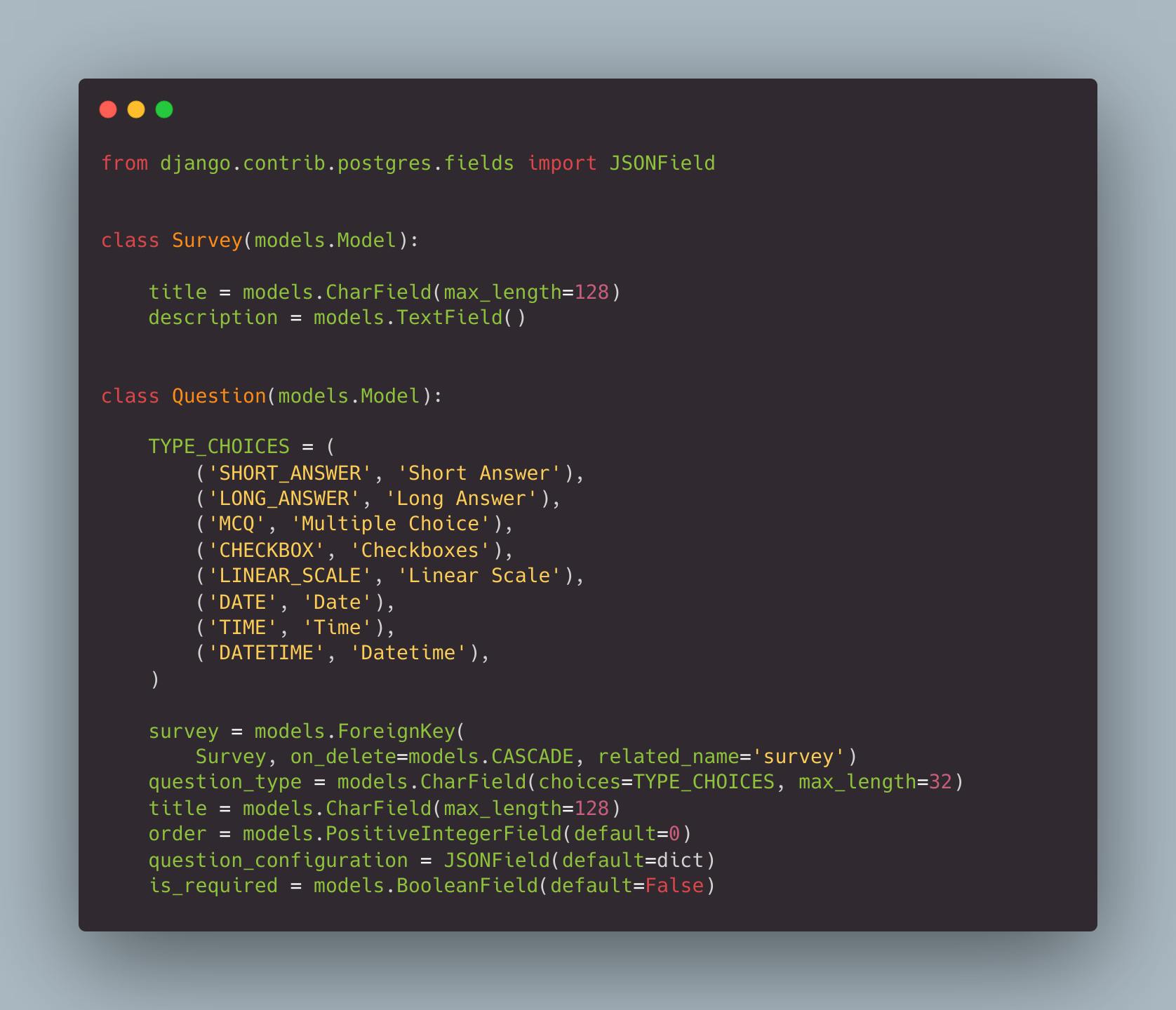
We will require more tables, but for our example, we need a Survey and a Question table.
In the Question table, we have a field called question_configuration where we can save a JSON related to the configuration selected with respect to the question type.
JSON configuration for an MCQ type question
{
"options": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "Mumbai" },
{ "id": 2, "title": "Chennai" },
{ "id": 3, "title": "Delhi" }
],
"is_add_other": true
}
The options key is a list of dictionaries/ objects storing the options. In each object, we have an id key and the title key storing the actual option value. If the is_add_other boolean option is set to true, then an input field of Other will be displayed below the options.
JSON configuration for a Checkbox type question
{
"options": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "Apples" },
{ "id": 2, "title": "Mangoes" },
{ "id": 3, "title": "Bananas" },
{ "id": 4, "title": "Grapes" }
],
"is_add_other": true,
"min_answers": 1,
"max_answers": 3
}
The min_answers key determines the minimum selected values required and the max_answers key determines the maximum selected options required to answer the question. All other options are similar to the MCQ question.
JSON configuration for a Linear Scale type question
{
"lowest_value": 1,
"highest_value": 5,
"lowest_value_label": "Bad",
"highest_value_label": "Excellent"
}
The lowest_value key determines the lowest value of the linear scale and the highest_value key determines the highest value of the linear scale. The lowest_value_label and the highest_value_label are for the labels.
JSON configuration for a Date type question
{
"min_date": "12/02/2020",
"max_date": "12/02/2021"
}
The min_date and the max_date are for specifying the range of dates. If set to null then the range will not be checked.
JSON configuration for a Time type question
{
"min_time": "09:00",
"max_time": "18:00"
}
Similar to the Date question, the min_time and the max_time are for setting a range if needed.
The json-schemas
Now we have an idea of what JSON we will require to store our data. The next item would be to create json-schemas for each of our question types.
The json-schema for MCQ type question
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"options": {
"type": "array",
"minItems": 0,
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "number"
},
"title": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"id",
"title"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"is_add_other": {
"type": "boolean"
}
},
"required": [
"options",
"is_add_other"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
For our MCQ configuration, the outermost level of the JSON is of type object. It has 2 required properties, so we add options and is_add_other to the required key. We set additionalProperties to false so that no new properties are allowed. In the properties key, we have to define the two properties of our object.
The is_add_other key is of the boolean type so we set the type to boolean. For the options key, we define that this object will contain only id and title.
The json-schema for Checkbox type question
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"options": {
"type": "array",
"minItems": 0,
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "number"
},
"title": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"id",
"title"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"is_add_other": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"min_answers": {
"type": "number"
},
"max_answers": {
"type": "number"
}
},
"required": [
"options",
"is_add_other",
"min_answers",
"max_answers"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
The checkbox type question's json-schema is similar to MCQ question. We just added min_answers and max_answers.
The json-schema for Linear Scale type question
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"lowest_value": {
"type": "number"
},
"highest_value": {
"type": "number"
},
"lowest_value_label": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
},
"highest_value_label": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
}
},
"required": [
"lowest_value",
"highest_value",
"lowest_value_label",
"highest_value_label"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
For the linear scale, we defined all the properties. Observe for the lowest_value_label and the highest_value_label keys, we have defined the type as string and null because we are accepting both.
The json-schema for Date type question
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"min_date": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
},
"max_date": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
}
},
"required": [
"min_date",
"max_date"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
For the date question, we can even have a pattern key at the type level where we can have the regular expression for the date format.
The json-schema for Time type question
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"min_time": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
},
"max_time": {
"type": ["string", "null"]
}
},
"required": [
"min_time",
"max_time"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
Here also we can have the pattern key where we can specify the regular expression for the time format.
The validation process
All we need to do is, take the JSON passed in the body of the API and take the json-schema for the question type and validate!
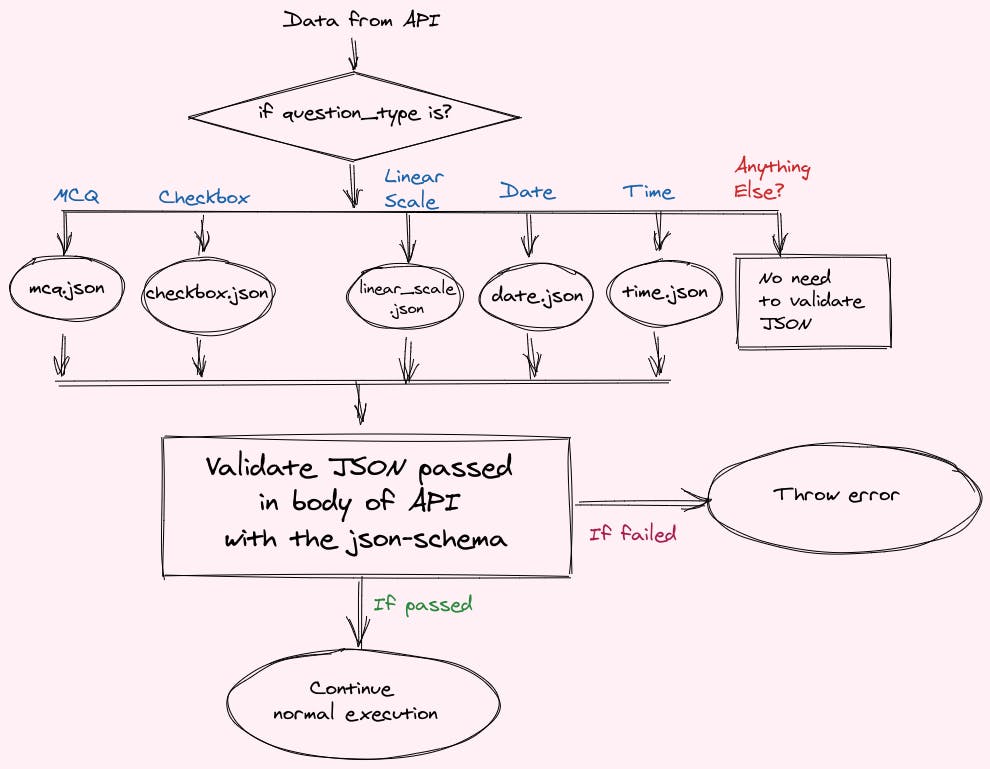
We can have a class that will just take the data to be validated and the file path of the JSON and validate both.

We will override the validate method of our serializer to validate the JSON according to the question type.
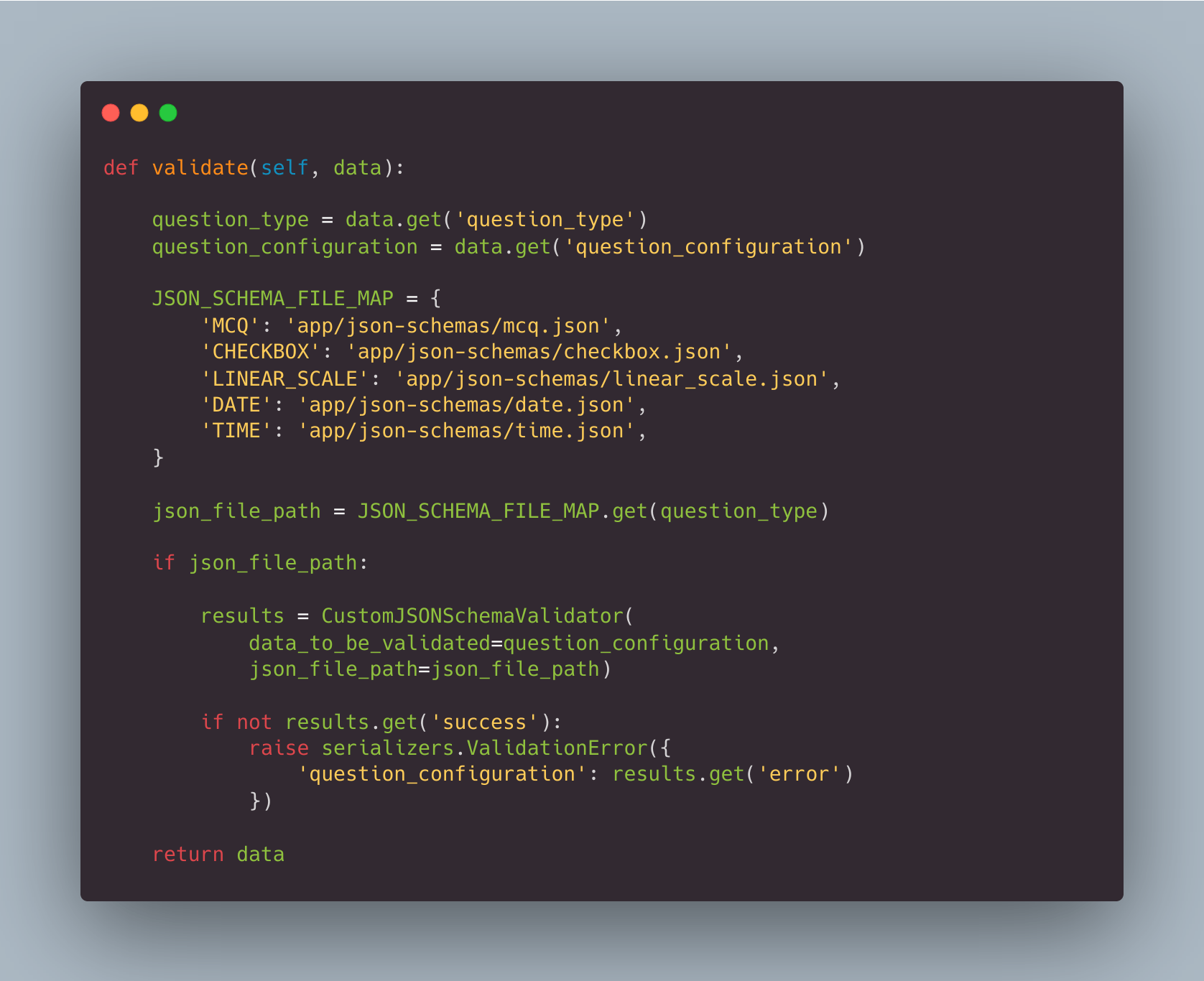
That's it. We are now validating our JSON as per our question types and we are sure that invalid data will not be stored in our JSON.
This was a json-schema implementation in Django and it supports many other languages as well.
Thanks for reading!

